Ovarian Cysts: What Every Woman Needs to Know
Ovarian cysts are common and often harmless, but some may cause discomfort or require medical attention. Understanding the types, symptoms, and treatment options is key to managing your reproductive health. Learn how early diagnosis can help prevent complications and when to seek care.
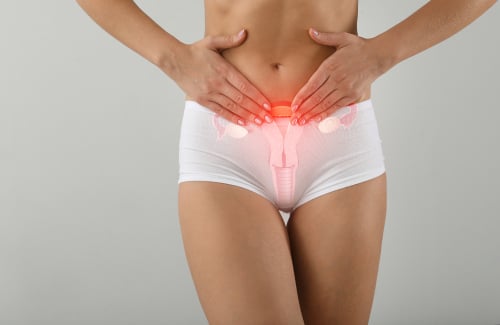
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop inside an ovary. While they are common and often harmless, proper diagnosis and monitoring are essential to ensure they don’t lead to complications. Most ovarian cysts disappear naturally, but some may persist and require medical attention.
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts form during the menstrual cycle and are usually benign (non-cancerous). They can occur at any age, but they are most commonly found in women of reproductive age. While many cysts resolve on their own, some can cause discomfort or signal underlying health conditions.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
There are several types of ovarian cysts, but the two most common are:
- Follicular Cysts – Your ovaries contain follicles that hold immature eggs. Each month, several eggs mature, and one is released during ovulation. If a follicle does not release its egg or fails to shrink after ovulation, it turns into a cyst. Fortunately, follicular cysts usually resolve within a few months without intervention.
- Corpus Luteum Cysts – After an egg is released, the remaining follicle transforms into a small mass of cells called the corpus luteum, which produces hormones to support a potential pregnancy. If the corpus luteum doesn’t shrink as expected, it can fill with fluid and form a cyst. These typically disappear within a few weeks.
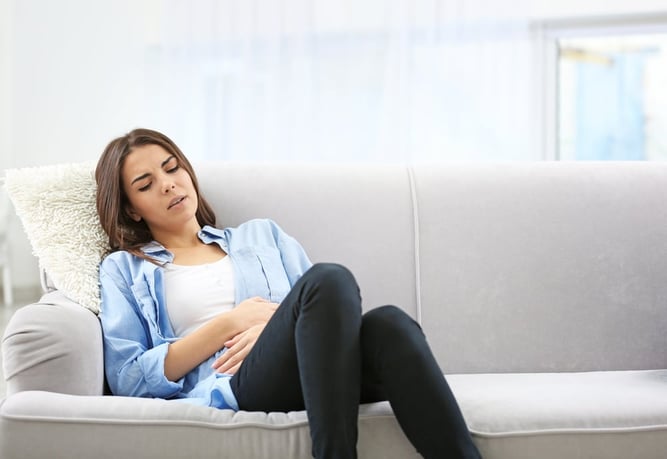
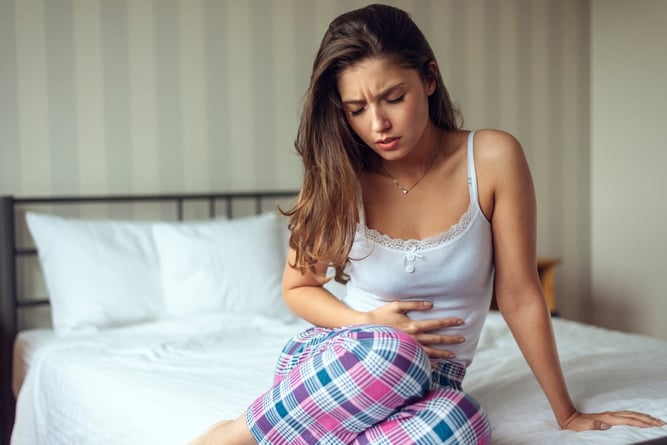
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
- Small ovarian cysts often don’t cause noticeable symptoms. However, as cysts grow larger, they can lead to:
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Bloating or a sense of fullness in the abdomen
- Painful intercourse
- Irregular menstrual cycles or spotting between periods
- Lower back pain
In rare cases, cysts may rupture or twist the ovary (ovarian torsion), leading to severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. If you experience intense pain or sudden symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Why Early Diagnosis Is Important
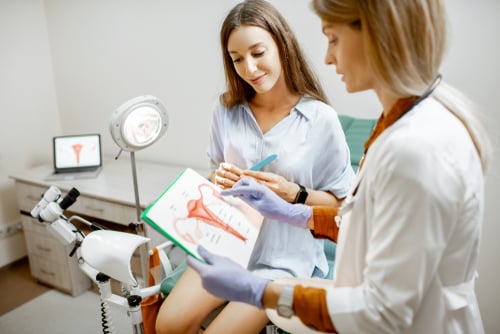
Most ovarian cysts are harmless, but some can indicate hormonal imbalances, endometriosis, or even ovarian cancer (though rare). That’s why routine gynecological exams and ultrasounds are crucial in detecting and monitoring cysts. If a cyst is persistent, large, or causing symptoms, your doctor may recommend further evaluation and treatment.
Treatment Options for Ovarian Cysts
The approach to treating ovarian cysts depends on their size, type, and symptoms:
- Watchful Waiting – Many cysts resolve on their own, so doctors may recommend monitoring through follow-up ultrasounds.
- Birth Control Pills – Hormonal birth control may help prevent the formation of new cysts by regulating ovulation.
- Surgical Removal – If a cyst is large, painful, or potentially cancerous, a doctor may recommend laparoscopic surgery to remove it.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience persistent pelvic pain, bloating, or menstrual irregularities, don’t ignore the symptoms. Seeking medical advice can help catch potential concerns early and provide peace of mind. At Garden OB/GYN, we provide expert care for women’s reproductive health.