Ovarian Cancer 101: Understanding the Basics
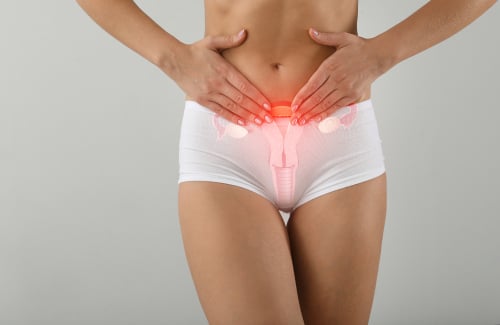
Ovarian cancer starts in the ovaries, small almond-shaped organs in the female reproductive system. It's a highly deadly gynecologic cancer often found in advanced stages, making it a formidable foe.

Every September, the world turns its attention to Ovarian Cancer Awareness Month, a crucial time to educate ourselves about this silent yet formidable disease. Ovarian cancer may not always make headlines, but its impact is undeniable. By delving into the fundamentals of ovarian cancer, we can raise awareness and promote early detection – a vital weapon in the fight against this often elusive enemy.
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer originates in the ovaries, those small, almond-shaped organs nestled within the female reproductive system. It is among the most lethal of gynecologic cancers and is frequently diagnosed in its advanced stages, making it a formidable adversary.
Why Early Detection Matters
The significance of early detection cannot be overstated. In the initial stages, ovarian cancer often remains asymptomatic, meaning there are no obvious signs or symptoms. By the time symptoms do appear, the cancer has typically progressed significantly, making it more challenging to treat effectively. Hence, raising awareness and advocating for proactive health screenings are critical in the battle against this disease.
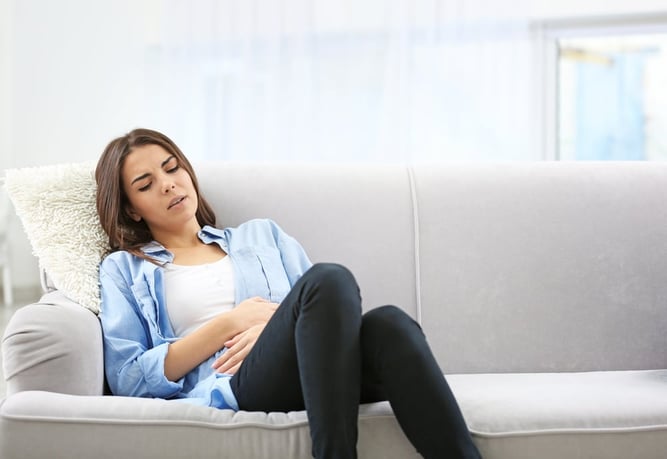
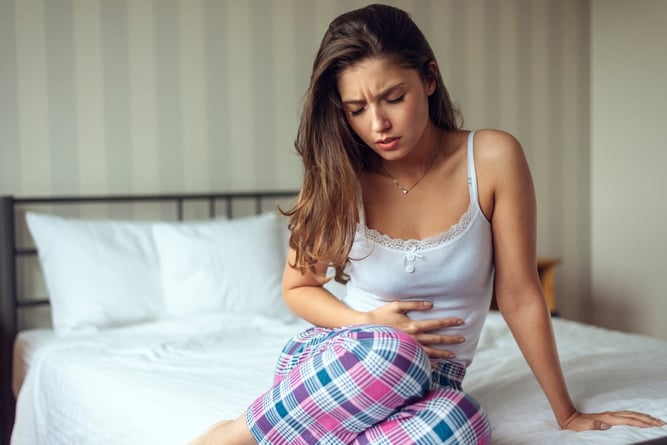
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms of ovarian cancer can be challenging as they tend to be subtle and can easily be mistaken for other, less severe health issues. Some of the common symptoms include:
- Persistent bloating: Feeling consistently bloated, even without a clear cause.
- Abdominal or pelvic pain: Unexplained discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis.
- Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly: Experiencing reduced appetite or a sensation of fullness after consuming only small amounts of food.
- Frequent urination: An increased need to urinate, often without relief.
- Changes in bowel habits: Unusual alterations in bowel movements.
- Unexplained fatigue: Overwhelming tiredness that doesn't improve with rest.
If any of these symptoms persist for more than a few weeks, it is imperative to consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Risk Factors
While ovarian cancer can affect anyone with ovaries, several factors may heighten an individual's risk:
- Family History: A strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer can elevate one's risk.
- BRCA Mutations: Inherited mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes can significantly increase susceptibility.
- Age: The risk of ovarian cancer rises with age, particularly after menopause.
- Endometriosis: Women with endometriosis may face a higher risk.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Long-term use of HRT may slightly increase the risk.
- Obesity: Carrying excess weight can also be a contributing factor.
Take Action Today
Awareness is the first step towards making a difference. Share this article to spread the word about ovarian cancer. Encourage regular check-ups, especially for those with risk factors or experiencing symptoms. Remember, early detection can save lives.
Let's unite during Ovarian Cancer Awareness Month to effect change, support one another, and strive for a future where ovarian cancer no longer claims lives without a fight. Together, we can make a difference.