Common Tests and Screenings During Pregnancy
Pregnancy, a transformative time, involves crucial tests ensuring a healthy journey for both mother and baby. Early detection and addressing potential issues are key for a smooth pregnancy and safe delivery.

Pregnancy is a transformative and exciting time for expectant parents, marked by a multitude of changes and preparations. Ensuring a healthy pregnancy and a safe delivery involves a series of tests and screenings that help monitor the well-being of both the mother and the developing baby. These assessments are crucial for detecting and addressing potential issues early on, promoting a smoother pregnancy journey.
- Prenatal Blood Tests:
One of the first steps in prenatal care involves a series of blood tests. These tests help assess the mother's overall health and identify any underlying conditions that might affect the pregnancy. Common blood tests include:
a. Blood Type and Rh Factor: Determining the blood type and Rh factor is essential to prevent Rh incompatibility issues between the mother and baby.
b. Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test assesses the levels of red and white blood cells, providing insights into the mother's overall health and detecting conditions like anemia.
c. Blood Glucose Screening: To check for gestational diabetes, a condition that can develop during pregnancy and affect both the mother and the baby.
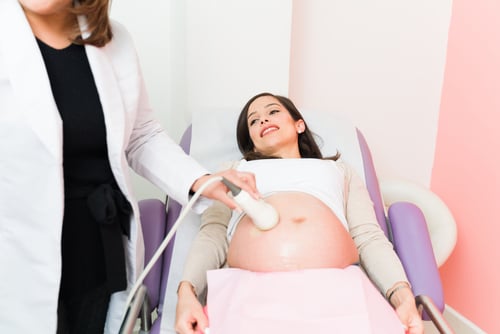
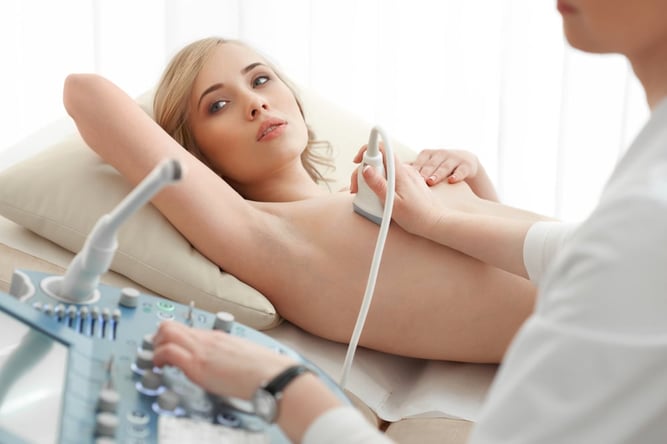
- Ultrasound Scans:
Ultrasound scans are a non-invasive way to visualize the developing baby and monitor its growth and development. Common types of ultrasound scans during pregnancy include:
a. Dating Scan: Typically performed in the first trimester, it helps determine the due date and confirms the number of embryos.
b. Anatomy Scan: Conducted around 18-20 weeks, this detailed scan checks the baby's organs, limbs, and overall development.
c. Doppler Ultrasound: Monitors blood flow to the baby, ensuring proper oxygen and nutrient supply.
- Genetic Testing:
Genetic tests are optional but can provide valuable information about the baby's risk for certain genetic conditions. These tests include:
a. Carrier Screening: Identifies if parents carry genes for certain genetic disorders, helping to assess the risk of the baby inheriting such conditions.
b. Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT): Screens for chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, through a simple blood test.
- Screening for Infections:
Various infections can pose a risk during pregnancy, and screening helps in their timely detection. Common screenings include:
a. Group B Streptococcus (GBS) Test: Identifies whether the mother carries GBS bacteria, which can cause complications during childbirth.
b. Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) Screening: Ensures early detection and treatment of infections like syphilis, HIV, and hepatitis, which can impact the baby's health.
- Monitoring High-Risk Conditions:
For women with pre-existing medical conditions or those who develop complications during pregnancy, additional monitoring may be necessary. This can include more frequent ultrasounds, specialized blood tests, and consultation with specialists to ensure the best possible outcome for both mother and baby.
Conclusion:
Navigating the world of prenatal care involves a series of tests and screenings designed to ensure the health and well-being of both the expectant mother and her baby. These assessments provide valuable information, enabling healthcare providers to address potential issues early on and offer appropriate care. By actively participating in these screenings, expectant parents contribute to a healthier and more secure pregnancy journey, setting the stage for a positive start to parenthood. Consult with Garden OB/GYN now.