Causes of Urinary Tract Infections
Let's delve into the various factors that contribute to the development of UTIs, shedding light on the reasons behind this common health issue.

Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are prevalent and can cause discomfort, pain, and inconvenience. Understanding the root causes of UTIs is crucial for prevention and effective management. In this article, we will delve into the various factors that contribute to the development of UTIs, shedding light on the reasons behind this common health issue.
-
Bacterial Invasion: UTIs are primarily caused by the invasion of bacteria into the urinary tract. The most common culprit is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which normally resides in the digestive tract but can find its way into the urethra. From there, it can ascend to the bladder and, in more severe cases, reach the kidneys.
-
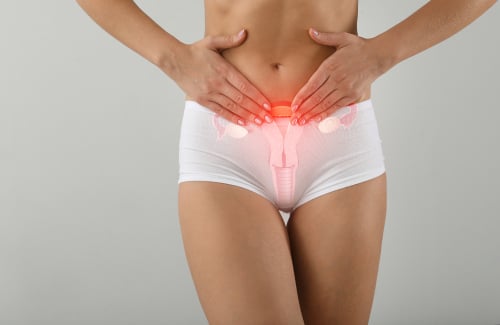
Female Anatomy: Women are more susceptible to UTIs due to their anatomy. The shorter urethra in females provides a shorter path for bacteria to travel from the outside to the bladder. This anatomical difference increases the likelihood of bacterial entry and subsequent infection.
-
Sexual Activity: Sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urethra, contributing to the development of UTIs. It's advisable to urinate after intercourse to help flush out any potential bacteria and reduce the risk of infection.
-
Menopause and Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes, particularly during menopause, can alter the urinary tract environment. The decline in estrogen levels can lead to changes in the vaginal flora, making it more susceptible to bacterial colonization and increasing the risk of UTIs.
-
Obstruction of Urine Flow: Anything that obstructs or impedes the flow of urine can contribute to UTIs. Conditions such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate in men can create a blockage, allowing bacteria to accumulate and cause infection.
-
Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, whether due to medical conditions or certain medications, are more susceptible to infections, including UTIs. A robust immune system plays a crucial role in warding off bacterial invaders.
-
Catheter Use: The use of urinary catheters, often in healthcare settings, can introduce bacteria directly into the bladder. Proper hygiene and care are essential to minimize the risk of catheter-associated UTIs.
-
Diabetes: People with diabetes are at an increased risk of UTIs due to elevated blood sugar levels. High glucose levels create an environment conducive to bacterial growth, making it easier for infections to take hold.
Understanding the causes of Urinary Tract Infections is pivotal for adopting preventive measures and seeking timely treatment. By addressing risk factors such as maintaining good personal hygiene, staying hydrated, and seeking medical advice when needed, individuals can significantly reduce their susceptibility to UTIs. Proactive steps, coupled with awareness, contribute to overall urinary tract health and well-being.